Also in this category
View more in Network FailoverNetwork Failover
Network redundancy is crucial to business success

Few enterprises have escaped reliance on information and communications technology (ICT) networks. Verticals from software to healthcare, financial management, retail, telecommunications, and government agencies rely on powerful and reliable networks to operate their businesses effectively. The proliferation of data-intensive business applications and cloud-based computing to support flexible business strategies and remote work, among other things, has made powerful and reliable networks a necessity for most businesses.
It’s not surprising, then, that so much emphasis has been placed on maximizing the quality and cost-effectiveness of enterprise connectivity options. Metrics such as bandwidth and latency are well-recognized and understood across many market sectors.
One metric that has slipped under some radars is network redundancy. Of course, many are fully aware of the importance of choosing a network that is highly reliable and will rarely go down, at least for long. The importance of network redundancy, ensuring that there is failover capacity that will allow an enterprise to continue operations when things don’t go as planned, is less well-recognized. This crucial capacity can mean the difference between business success and failure.
Learn more about Inseego's network redundancy solutionNetwork redundancy is an investment in reliability, continuity, and against data loss
Network redundancy uses duplicate systems, connections, or paths in a network to ensure that if one component fails, another is available to take its place. This requires having additional hardware, software, or connections in place to provide backup and failover capabilities in case of a network outage.
A key value of network redundancy is that it minimizes downtime, which can lead to lost productivity, revenue, and, in some industries, potential legal consequences. Redundant systems and connections ensure that networks and infrastructure are not downed by a single failure.
Network redundancy also helps maintain continuity even during times of network disruption. Many consumers expect businesses to always be connected and available, and redundancy is crucial to meeting that expectation and maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. This is especially critical for industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail, where constant network availability is needed to provide services and maintain customer trust.
With redundant networks, businesses can also protect against the loss of sensitive data. If an outage happens, redundant backup systems can help prevent the loss or compromise of critical data, avoiding potential legal and financial consequences.
Finally, businesses must consider the opportunity costs associated with network failures and downtime. Customers or partners that approach a business and find they get no response, or that their inquiry is lost in the shuffle as the enterprise catches up from an outage, likely won’t put in the effort to follow up.
Incorporate both fault tolerance and high availability
Ensuring comprehensive network redundancy that is sufficient to maintain business continuity irrespective of outside factors isn’t easy. There are two essential components of a fully comprehensive network redundancy strategy: fault tolerance and high availability.
Fault tolerance uses duplicate systems or components to take over workloads if the primary unit fails. This can involve methods such as mirroring, where data is replicated in real-time between two devices, or clustering, where multiple servers work together to provide backup and load balancing capabilities.
High availability focuses on providing continuous network connectivity and access to critical systems using multiple connections or paths in the network. High availability strategies often involve load balancing and failover mechanisms, where traffic is rerouted to an alternate connection during a network failure.
Redundancy involves hardware, software, and connectivity
The two components of a comprehensive redundancy strategy are supported by three key pieces of infrastructure: hardware, software, and connectivity.
Hardware refers to duplicate network devices, such as routers, switches, and servers. Redundant hardware can be achieved through various methods, such as using dual power supplies, multiple processors, or different equipment from different vendors. This ensures that if one component fails, the network can continue to function without interruption.
Learn more about Inseego's hardware & software for network redundancyEffective redundancy also requires having backup copies of critical software applications and operating systems ready to immediately take over. This can also include failover systems, which automatically switch to a backup copy of the software, as well as load balancing systems, which distribute the workloads across multiple systems to prevent overload and potential failure.
Enterprises also need redundant connections. Multiple physical connections to the network, such as multiple network cables, ensure network connectivity is maintained even if one cable is damaged or otherwise rendered non-functional. Redundant connections are particularly important for high-traffic networks, where a single failure could result in significant downtime and loss of productivity.
Effective implementation requires a methodical approach
- To establish network redundancy, it is important to first identify the critical components of the network that must be redundant to ensure business continuity. This may include switches, routers, firewalls, servers, and other network devices that are essential for your businesses day-to-day operations.
- The next step is to determine the best type of redundant network infrastructure for your business. This can include options such as physical redundancy (duplicating network devices) or logical redundancy (using load balancing or failover mechanisms). Consider factors such as cost, complexity, and scalability when deciding on the right solution for your business.
- Backup connections are also important to consider. This can include secondary internet service providers, wireless connections, or satellite connections. These backup connections can provide an alternative means of network connectivity in case of a primary connection failure.
- In the event of a primary network failure, it is essential to have a failover plan in place. This plan should include a detailed explanation of how to switch to the backup network, how to reroute traffic, and how to keep downtime to a minimum.
- Once your redundant network is set up, it is important to regularly monitor and maintain it. This includes conducting regular audits, software updates, and performance tests to ensure that network redundancy capabilities are functioning properly and providing the necessary level of protection for your business.
Inseego supports every element of cost-effective network redundancy
Inseego provides businesses with comprehensive network redundancy solutions to ensure uninterrupted connectivity and business operations.
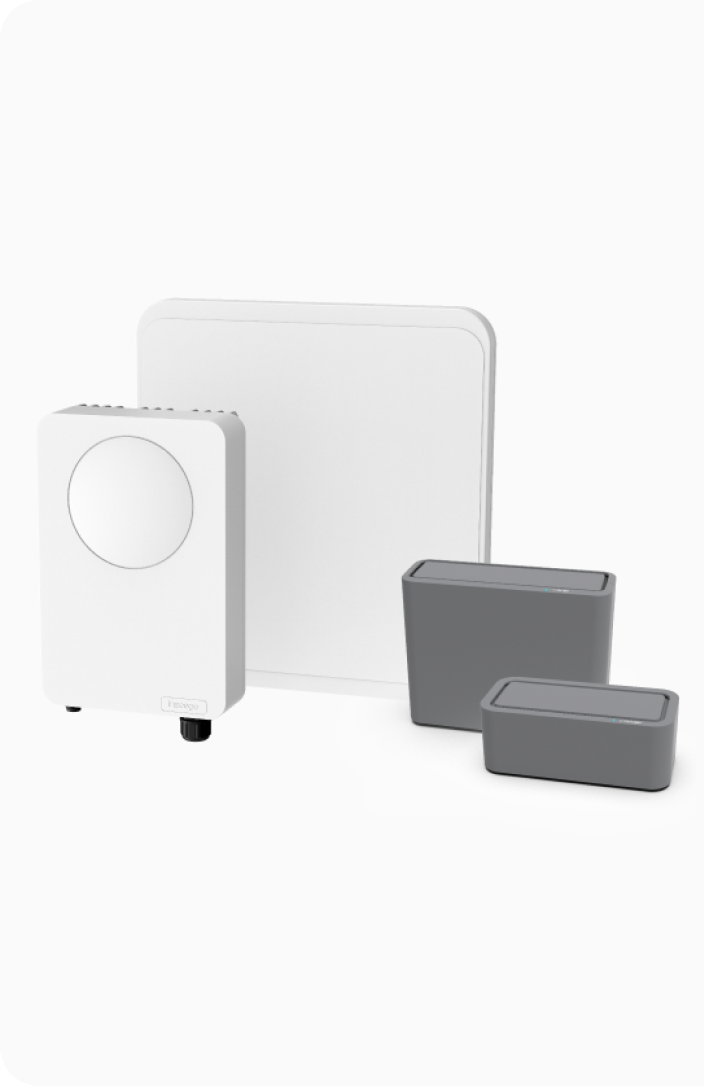
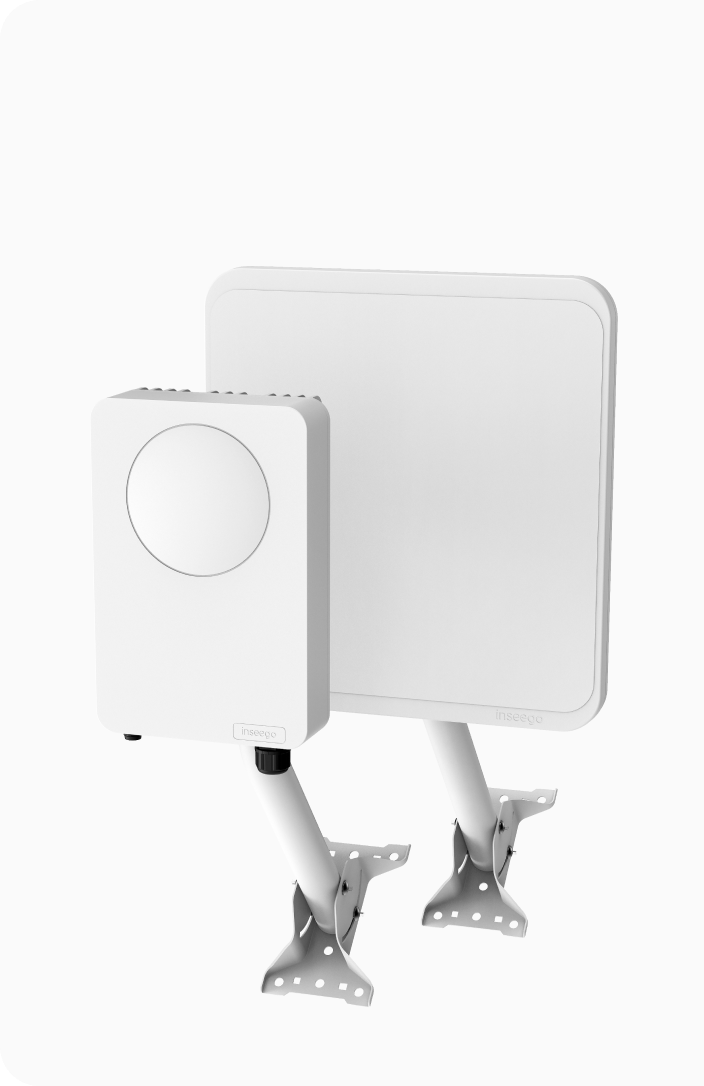
Multiple WAN connections can be used simultaneously, providing redundancy if one connection fails. Our 5G cellular routers act as secondary connections that are automatically switched over to in case of a network outage, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity for critical business operations. Dual-SIM capabilities combined with multi-carrier support across 4G/LTE, 5G, and Wi-Fi allow for seamless and reliable carryover between carriers, cellular connections, and wireless networks as needed.
Learn more about indoor cellular routersThe FX3100 5G cellular router is a perfect example of our redundancy solutions. It provides robust cellular connectivity which seamlessly integrates with existing infrastructure. With its dual-SIM and multi-WAN capabilities, the FX3100 ensures effective failover. Its cellular versatility also makes it ideal for businesses seeking to optimize network performance in remote and urban areas.
Learn more about our FX3100 5G cellular routerWe also offer cloud management solution through Inseego Connect which provides real-time network monitoring and management tools, allowing businesses to proactively identify and resolve any network issues before they can impact operations. This cloud management solution comes with Software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) to provide intelligent routing and load balancing, automatically directing traffic to the best-performing internet connection.
Learn more about Inseego ConnectContact us to speak with our experts and find out how to build the right network redundancy solution for your business.
Do you currently have a failover solution?
What are you using for failover?
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to cable
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to fiber
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to satellite
Are you interested in using cellular for failover instead?
Cellular is an ideal failover solution for businesses
Are you interested in using cellular as failover for your business?
Besides failover, are you interested in using cellular for flexible or temporary internet?
Even if temporary internet isn’t a focus, would you be interested in using cellular for cost-effective scalability?
Here's some resources
Here's the solution for failover!
Here's a cost-effective solution!
Here's the solution for temporary internet!
What are your details?
How can we contact you?














Did you know?
Our hugely experienced team are located across the USA.
We’ll connect you with the Inseego team member nearest to you.
What happens next?
We aim to contact you via email within 1 business day to arrange a suitable to time for a detailed discussion of your needs.