Also in this category
View more in Network FailoverNetwork Failover
Ensure business uptime with automatic failover
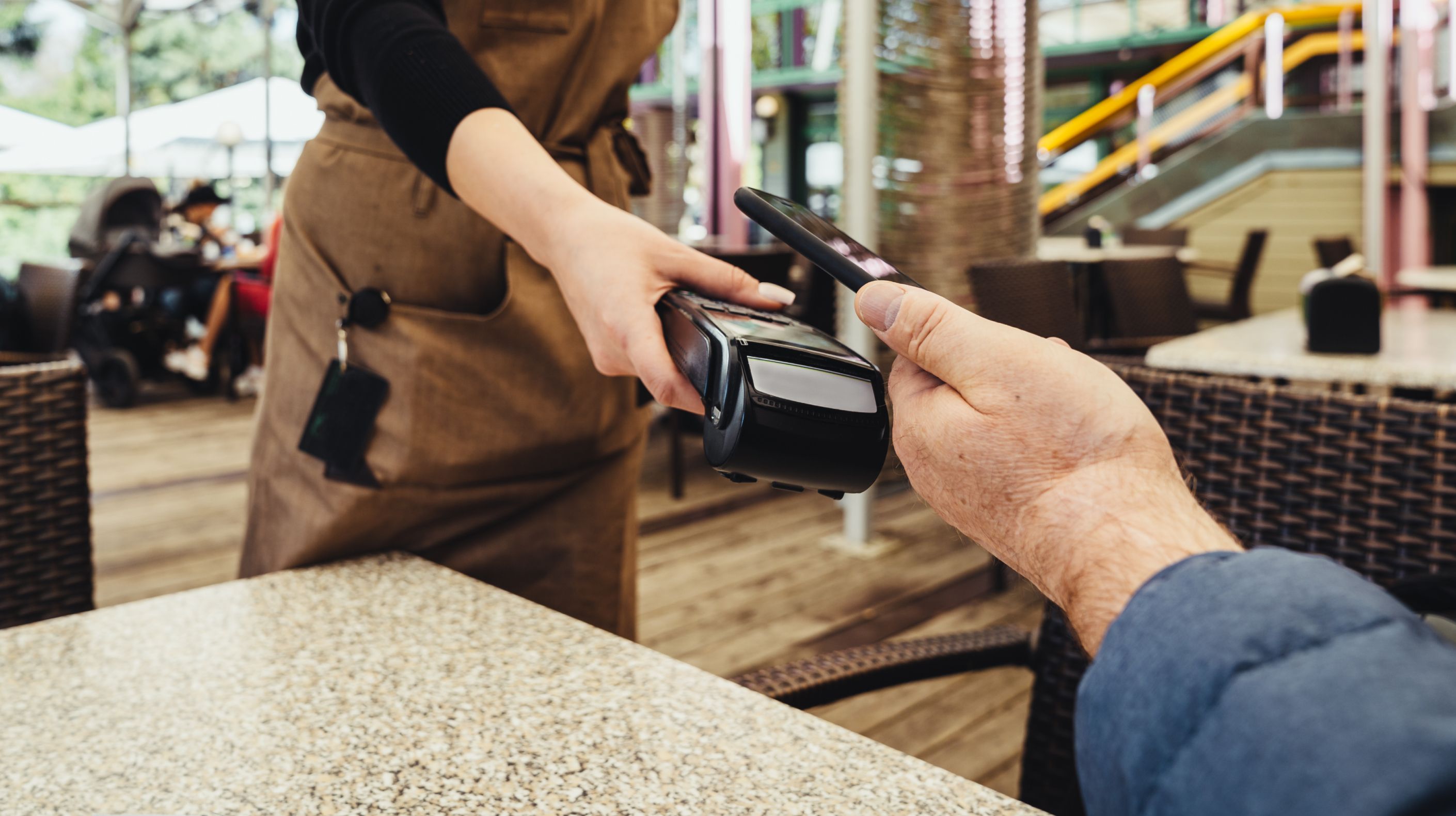

Network outages are a costly problem for today’s businesses. Even short periods of downtime can have a significant impact on operations, resulting in revenue losses and disruptions that can negatively affect the user experience for both customers and employees.
One way businesses can mitigate the impact of unexpected outages and downtime is with network failover. With a failover strategy, network traffic can be shifted to another network connection if the primary connection slows down or fails, thereby reducing the impact of outages on operations.
Automatic failover is the most reliable and efficient form of failover. It ensures businesses can maintain normal workflows, access necessary data, support internal and external communications, and conduct business irrespective of network conditions.
Automatic failover offers key advantages over manual failover
The process of moving traffic from a primary connection to a backup connection during a disruption can be either manual or automatic. The crucial difference between automated failover and manual failover is speed. Automatic failover is faster, as a computer can respond in real-time to adjust network traffic as necessary, minimizing disruption and downtime.
An automatic failover process provides three key advantages:
- Minimized downtime: Automatic failover significantly reduces downtime by promptly switching to a backup connection without requiring manual intervention.
- Maximized productivity: With networks continuing to remain functional, employees remain productive and customers don’t experience any loss of service due to endpoint failure.
- Cost savings: The delays associated with manual failover can extend costly downtime. With an automatic solution, network switching happens faster, mitigating or eliminating the financial impact of downtime.
Failover can operate actively or passively
Another important distinction is between active and passive forms of network failover.
Active failover ensures all available primary and secondary network connections are always active. Traffic can always be distributed across both networks as needed and is automatically rerouted when or if network connections are disrupted or go down. This approach provides extremely reliable redundancy and enhances traffic management with load balancing but is generally more costly.
Passive failover ensures that traffic flows through one active primary connection at all times. Secondary network connections wait passively on standby and become active only if the primary connection goes down. This approach is very cost-effective, with minimal resource consumption until failover occurs.
Failover process and troubleshooting should be planned in advance
While a network failover solution can provide substantial value once it’s up and running, it’s crucial to prepare for potential disruptions in advance to ensure the solution delivers value when it is needed. Careful planning can mean the difference between seamless business continuity and disruptive downtime. A meticulous approach can help reduce the impact of unexpected outages and enhance overall data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
An effective failover strategy should include procedures for regular network testing, updating, and maintenance, as well as a detailed failover plan of action that will be followed when a disruption occurs.
Regular testing should include:
- Routine simulations: Conduct regular network failover simulations to ensure that all systems trigger and switch correctly during an actual outage. This includes testing every aspect of the failover process, from failure detection to the activation of the standby internet connection.
- Load testing: Mimic real-world workloads to test the performance of the standby connection under typical operational conditions. Ensure that the new primary connection can handle the required load without compromising performance.
- Recovery drills: Conduct full recovery drills that simulate both failover and failback processes. These drills help verify that your systems can return to the original primary connection without data loss or significant latency.
- Document results: Keep detailed records of all test results, including any issues encountered and the steps taken to resolve them. This information is invaluable for optimizing future failover operations.
Plans for updating and maintenance should include:
- Software updates: Regular updates to both the primary and standby systems with the latest software patches and security updates minimize vulnerabilities and ensure compatibility with the latest technologies.
- Hardware checks: Periodic inspection and proactive maintenance of the physical hardware components involved in the failover system can prevent potential failures that software updates alone might not address.
- Configuration audits: Conduct routine audits of all configurations, including failover clusters, replication settings, and data synchronization parameters, to ensure alignment with the latest best practices and organizational requirements.
- Backups: Maintain up-to-date backups of all critical data, including configuration files, to ensure that systems can be quickly restored in case of failure. Verify that these backups are consistently synchronized between the primary and standby systems.
Finally, it’s very important to establish clear failover policies, such as:
- Detailed failover plan: Develop and document a comprehensive failover plan that details each step of the failover process. This plan should include trigger points, necessary actions, responsible personnel, and communication protocols.
- Notification systems: Implement robust notification systems that alert IT staff and relevant stakeholders about failover events. These notifications should include real-time updates and clear instructions for manual intervention if required.
- Roles and responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of all team members involved in managing and executing failover procedures. Ensure that everyone understands their duties and has received appropriate training.
- Policy reviews: Regularly review and update failover policies to reflect changes in the IT environment, organizational goals, or emerging best practices. Include feedback from previous failover events to continuously improve policies.
By adhering to these best practices, businesses can ensure a robust and efficient automatic failover process that minimizes downtime and maintains high availability.
Inseego provides robust and reliable failover solutions
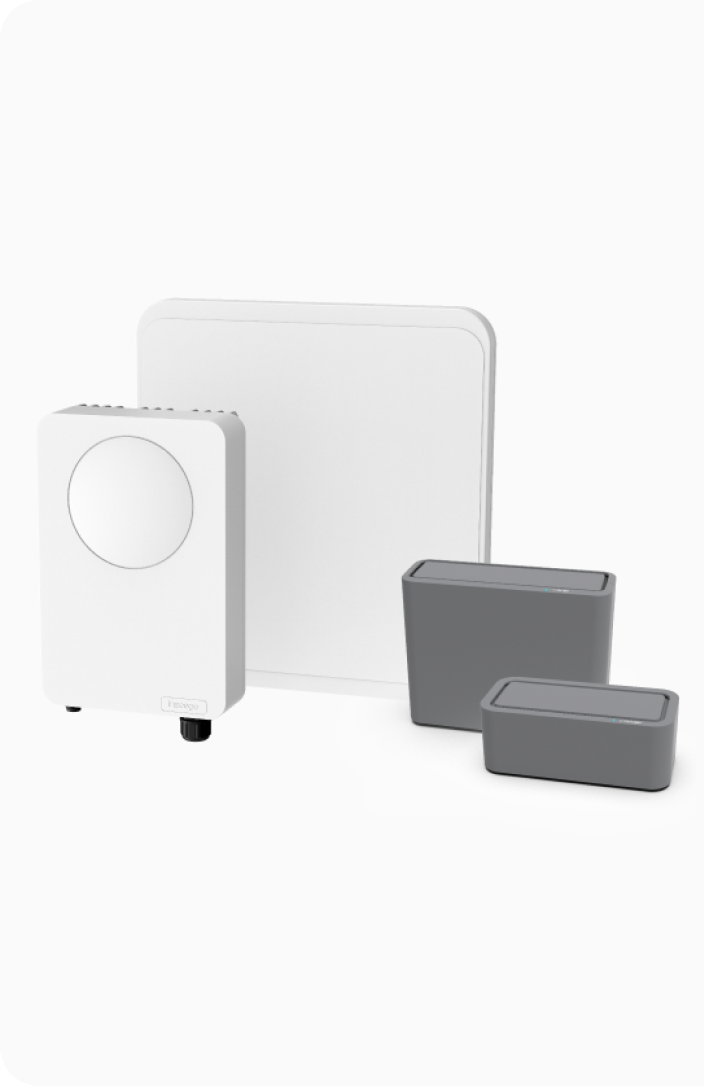
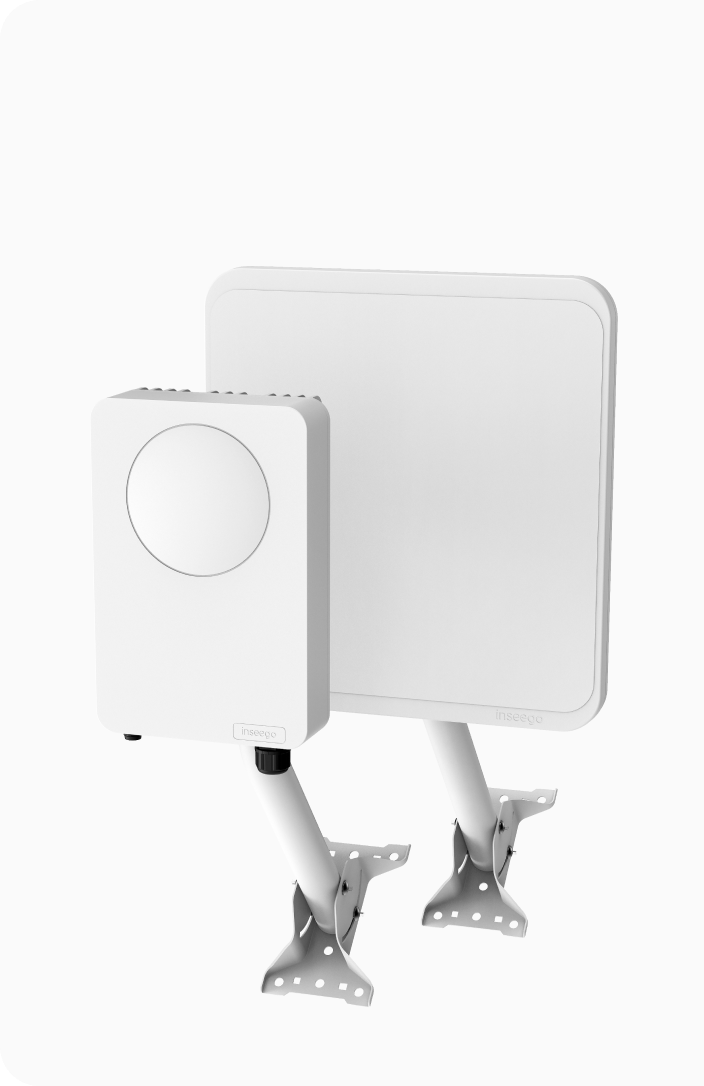
Inseego offers indoor and outdoor automatic failover solutions to help businesses maintain high availability and seamless operations during network disruptions.
The Inseego Wavemaker™ PRO 5G outdoor cellular antenna CPE FW3000 offers robust failover capabilities to ensure continuous internet connectivity. The FW3000 is a high-performance IP67-rated weatherproof and temperature-resistant device designed for reliable internet access through cellular connectivity outdoors, in rural and remote locations.
Learn more about the FW3000 outdoor cellular antennaThe Inseego Wavemaker™ PRO 5G indoor cellular router FX3100 series is designed to ensure high-speed, reliable connectivity with robust failover capabilities. These routers deliver tailored high-speed 5G connectivity for business environments. They provide automatic failover between dual SIM cards or between WAN ports of a primary router to a secondary router to maintain service continuity during primary network outages.
Learn more about the FX3100 indoor cellular routerIf you’re considering upgrading your current network system, consult with our experts to understand the best failover solution for your needs.
Do you currently have a failover solution?
What are you using for failover?
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to cable
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to fiber
Cellular provides a superior failover option compared to satellite
Are you interested in using cellular for failover instead?
Cellular is an ideal failover solution for businesses
Are you interested in using cellular as failover for your business?
Besides failover, are you interested in using cellular for flexible or temporary internet?
Even if temporary internet isn’t a focus, would you be interested in using cellular for cost-effective scalability?
Here's some resources
Here's the solution for failover!
Here's a cost-effective solution!
Here's the solution for temporary internet!
What are your details?
How can we contact you?














Did you know?
Our hugely experienced team are located across the USA.
We’ll connect you with the Inseego team member nearest to you.
What happens next?
We aim to contact you via email within 1 business day to arrange a suitable to time for a detailed discussion of your needs.